
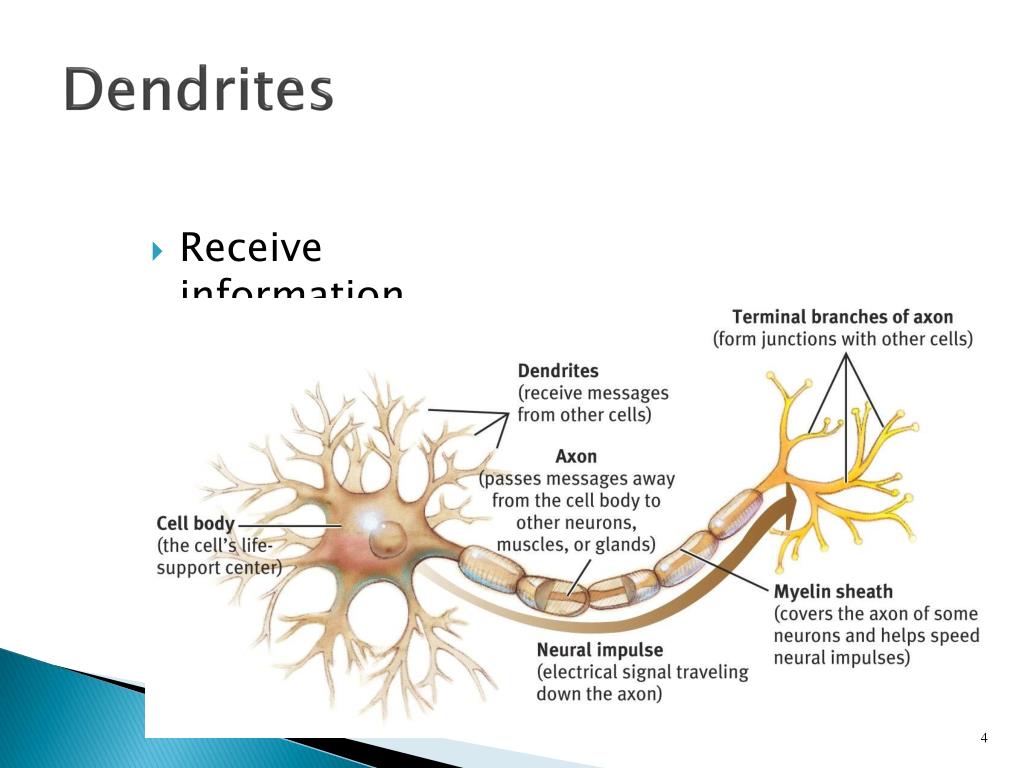
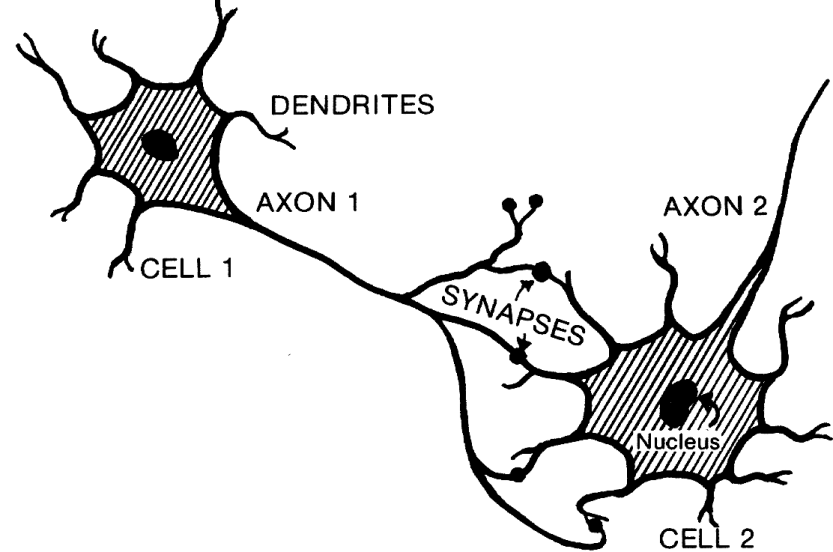

The axon (tree roots) is the output structure of the neuron when a neuron wants to talk to another neuron, it sends an electrical message called an action potential throughout the entire axon. Dendrites branch as they move towards their tips, just like tree branches do, and they even have leaf-like structures on them called spines. A dendrite (tree branch) is where a neuron receives input from other cells. A neuron has three main parts: dendrites, an axon, and a cell body or soma (see image below), which can be represented as the branches, roots and trunk of a tree, respectively. What does a neuron look like?Ī useful analogy is to think of a neuron as a tree. The creation of new neurons in the brain is called neurogenesis, and this can happen even in adults. Having said that, our roughly 100 billion neurons do interact closely with other cell types, broadly classified as glia (these may actually outnumber neurons, although it’s not really known). More than that, their interactions define who we are as people. Neurons (also called neurones or nerve cells) are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, the cells responsible for receiving sensory input from the external world, for sending motor commands to our muscles, and for transforming and relaying the electrical signals at every step in between.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
